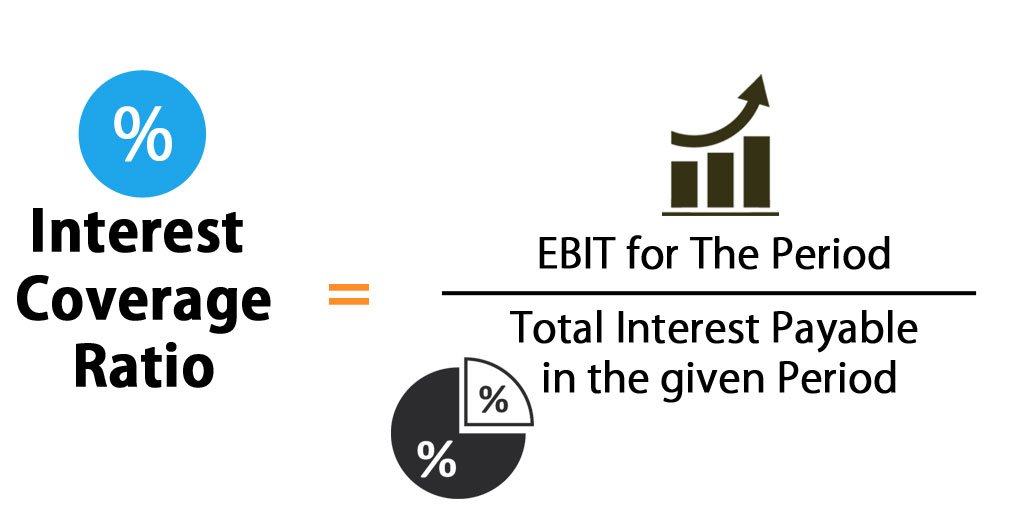
The interest coverage ratios is a financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to make interest payments on its debt. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses for a given period of time.
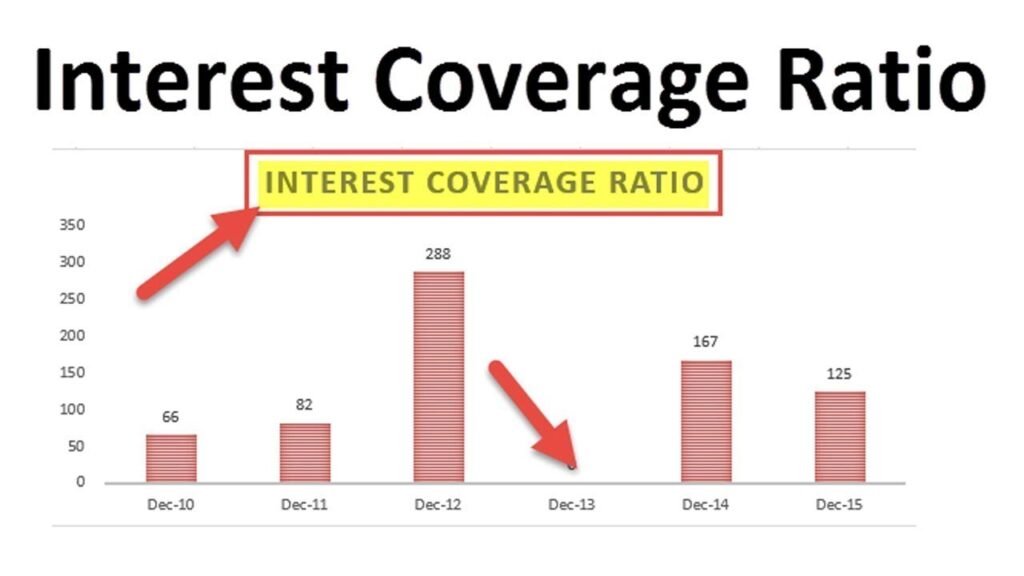
A high interest coverage ratio indicates that a company has plenty of earnings to make its interest payments, while a low ratio indicates that a company may have difficulty making its interest payments. The interest coverage ratio is just one tool that investors can use to assess a company’s financial health. In this article, we will take a closer look at the interest coverage ratio and what it can tell us about a company.
Types of Interest Coverage Ratios
There are several different types of interest coverage ratios that can be used to measure a company’s ability to make its debt payments. The most common type of interest coverage ratio is the interest expense coverage ratio, which measures the amount of income available to cover interest expenses.
Other types of interest coverage ratios include the operating cash flow interest coverage ratio and the capitalized interest coverage ratio.
The interest expense coverage ratio is the most common type of interest coverage ratio. This ratio measures the amount of income available to cover interest expenses. The formula for this ratio is:
Interest Expense Coverage Ratio = Income Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) / Interest Expense
A company with a high interest expense coverage ratio is considered to be financially healthy and able to make its debt payments. A low interest expense coverage ratio may indicate that a company is having difficulty meeting its debt obligations.
The operating cash flow interest coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to make its debt payments from its operating cash flow.
This ratio is important because it shows how well a company can generate cash from its normal business operations to meet its financial obligations. The formula for this ratio is:
Operating Cash Flow Interest Coverage Ratio = Operating Cash Flow / Interest Expense
A company with a high operating cash flow interest coverage ratio is considered to be financially healthy and able to make its debt payments from its normal business operations. A low operating cash flow interest coverage ratio may indicate that a company is having
What is the Interest Coverage Ratios?
The interest coverage ratio, also known as the debt service coverage ratio, is a financial ratio that is used to determine whether a company has the ability to pay its interest expenses on its outstanding debt.
The interest coverage ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses. A company with a high interest coverage ratio is able to make its interest payments with ease, while a company with a low interest coverage ratio may have difficulty meeting its interest payments.
Investors often use the interest coverage ratio as a tool to assess the financial health of a company. A company with a strong interest coverage ratio is typically viewed as being in good financial health, while a company with a weak interest coverage ratio may be viewed as being in poor financial health.
The interest coverage ratio is an important financial ratios for lenders because it indicates how well a borrower can make their required debt payments. Lenders want to lend money to borrowers who they believe will be able to repay their loans, and the interest coverage ratio can be used as one metric to assess this ability.
Generally speaking, a borrower with an interest coverage ratio of 2.0 or higher is considered to be financially healthy and capable of making their required debt payments on time. A borrower with an interest coverage ratio below 2.0 may be considered to be financially unhealthy and at risk of defaulting on their loan payments.
How to calculate the Interest Coverage Ratios
The interest coverage ratio is a financial metric used to calculate a company’s ability to pay its interest expenses on its debt. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its total interest expenses. A high interest coverage ratio indicates that a company can easily make its interest payments, while a low ratio indicates that the company may have difficulty making its payments.

To calculate the interest coverage ratio, first find a company’s EBIT. This can be found on the income statement. Then, find the company’s total interest expense for the same period of time. This figure can also be found on the income statement. Finally, divide the EBIT by the total interest expense. This number will be the interest coverage ratio.
For example, let’s say Company XYZ has an EBIT of $1 million and total interest expense of $500,000. This gives us an interest coverage ratio of 2 ($1 million/$500,000). This means that for every $1 in interest expense, Company XYZ has $2 in earnings before taxes to cover it. In general, an ICR above 1 is considered good because it means the company has enough earnings to cover its interest payments.
What is a Good Interest Coverage Ratios?
The interest coverage ratio is a financial ratio that is used to determine the ability of a company to pay interest on its outstanding debt. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expense. A company with a high interest coverage ratio is considered to be financially healthy and able to meet its debt obligations.
A good interest coverage ratio is typically above 3.0. This means that the company is generating enough income to cover its interest expenses three times over. A lower ratio may indicate that the company is struggling to meet its debt obligations and may be at risk of defaulting on its loans.
How to Improve Your Interest Coverage Ratios
The interest coverage ratio is a financial metric used to assess a company’s ability to make its debt payments. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses. A high ratio indicates that a company has plenty of earnings to cover its interest expenses, while a low ratio indicates that a company may have difficulty making its debt payments.
There are several ways to improve your interest coverage ratios:
- Increase your EBIT: One way to improve your interest coverage ratio is to increase your EBIT. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as increasing sales, reducing costs, or improving efficiency.
- Decrease your interest expenses: Another way to improve your interest coverage ratio is to decrease your interest expenses. This can be done by refinancing at a lower rate, prepaying some of your debt, or negotiating with creditors for lower rates.
- Increase your equity: A third way to improve your interest coverage ratio is to increase your equity. This can be done by issuing new shares of stock, retained earnings, or borrowing money.
Improving your interest coverage ratio is important because it can help you secure financing in the future and show creditors that you’re a responsible borrower. If you have any questions about how to improve your interest coverage ratio, please contact us today!
Also Read: What Is a Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement

