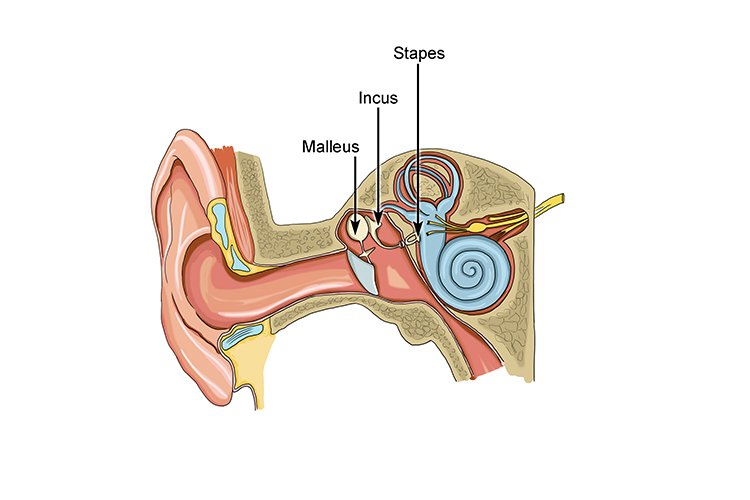
The human body is made up of a skeletal structure of bones including both long and short bones. While the thigh bone is clearly the largest bone in the body, the Stapes or Stirrup bone in your middle ear is the tiniest and softest. It is critical in transporting sound waves through the outer ear to your internal ear.
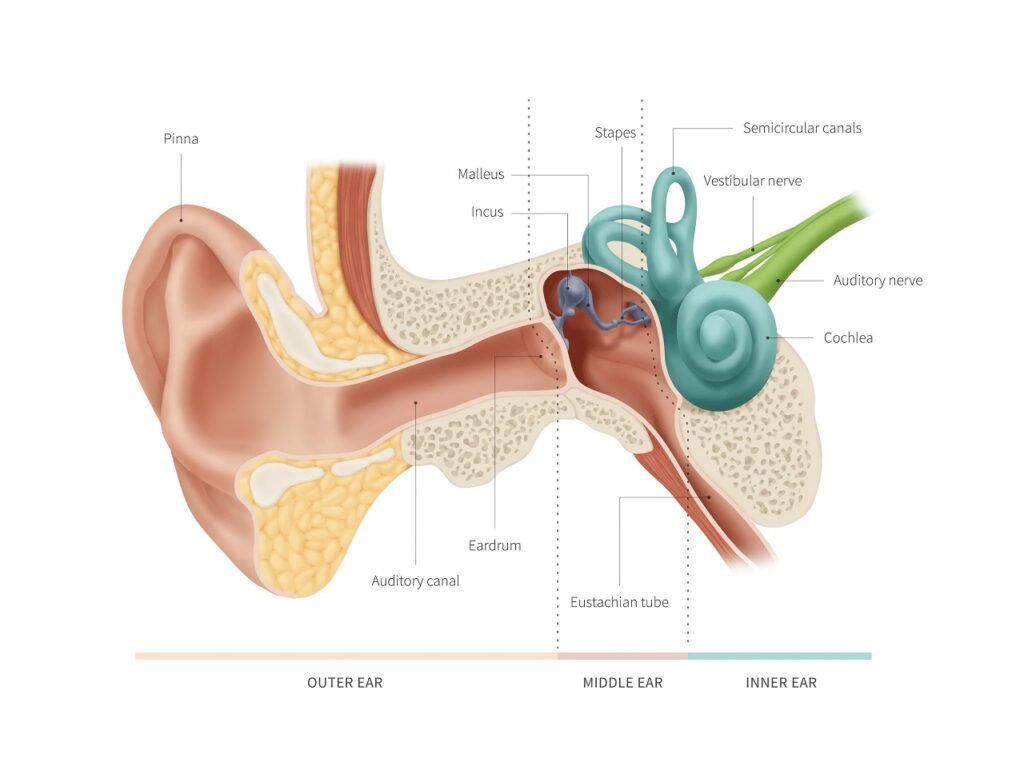
As we all understand, sounds are a sort of energy that requires a physical carrier to move. The resulting sound by a pulsating stimulus passes via airflow and hits the ear’s outer layer. The auricle catches all acoustic signals and sends them to the inner ear. Vibrations that come in contact with the eardrum cause disturbance in the eardrum, and cause all of the ear ossicles to vibrate.
The term “ear ossicles” consists of 3 microscopic middle ear bones that aid in the transmission of sound intensity between the air-filled cavities to the fluid-filled cavity. The Stapes is the smallest type of middle ear bone fragment (approx 3 x 2.5mm).
Function of Stapes
The stapes is a membrane-covered bone barrier that divides the inner and middle ear. The principal task of the stapes is to enhance sound waves, which is crucial in moving the fluids of the inner ear. This causes neuro impulses to be induced in sensory nerve fibers, allowing data about the resonant spectrum of the audio to be encoded and conveyed to the brain.
When the Pinna or Auricle transmits audio signals to the auditory canal, the eardrum, which really is adequately responsive to register even the slightest wave, copies the pulses and causes the Malleus to vibrate as well. Mechanical vibration travels from the eardrum to the malleus and from there to the anvil. The tiniest bone, Stapes or Stirrup, enhances the vibrations imparted by Anvil.
Because of the enhancement of this resonance, the fluid in the cochlea begins to vibrate like a wave, activating the microscopic hair cells in the cochlea. Each cell corresponds to a certain wavelength. So when vibrations travel through the hair cells, the cells register the wavelength of the vibrations and convert it to electrical impulses, that are transmitted to the brain across the inner ear.
The brain recognizes the signal and determines where it came from. That’s how the sound pressure wave is transformed into a brain electric signal, allowing humans to perceive all audio input generated by various sources.
What is the Significance of Stapes Size?
Because the audio vibrations collected by Malleus from the eardrum must be boosted, the final bone of the ear ossicles (i,e Stapes) must be the shortest in length. The shorter the bone, the greater the sound is amplified. Stapes is a mechanical advantageous mechanism that is used to transport a large sound signal across a short-range by delivering a lesser strain.
Since the audio generated by the origin is generally distant and weak, the intensity impacting the ear is considered to be lesser. As a result of the Stapes’ tiny size, the ear is able to create a significant pressure from a little input force to help with receiving the audio signals effectively or simply, hearing.
Any issue with the middle ear or stapes will lead to reduced vibrations and ineffective audio signal transmission to the Cochlea in the inner ear. As a consequence of the shortage of appropriate audio vibrations transmission, the ensuing audio perceived would be of poor frequency.